Interpretable prediction
Designing interpretable goal recognition for autonomous vehicles
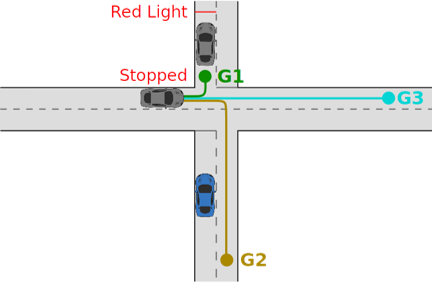
Goal recognition (GR) involves inferring the goals of other vehicles, such as a certain junction exit, which can enable more accurate prediction of their future behaviour. In autonomous driving, vehicles can encounter many different scenarios and the environment may be partially observable due to occlusions.
In this project, we present a novel GR method named Goal Recognition with Interpretable Trees under Occlusion (OGRIT)[paper[video]. OGRIT uses decision trees learned from vehicle trajectory data to infer the probabilities of a set of generated goals. We demonstrate that OGRIT can handle missing data due to occlusions and make inferences across multiple scenarios using the same learned decision trees, while being computationally fast, accurate, interpretable and verifiable.

Our research was also reported by Five AI/Bosch. More information can be found here.